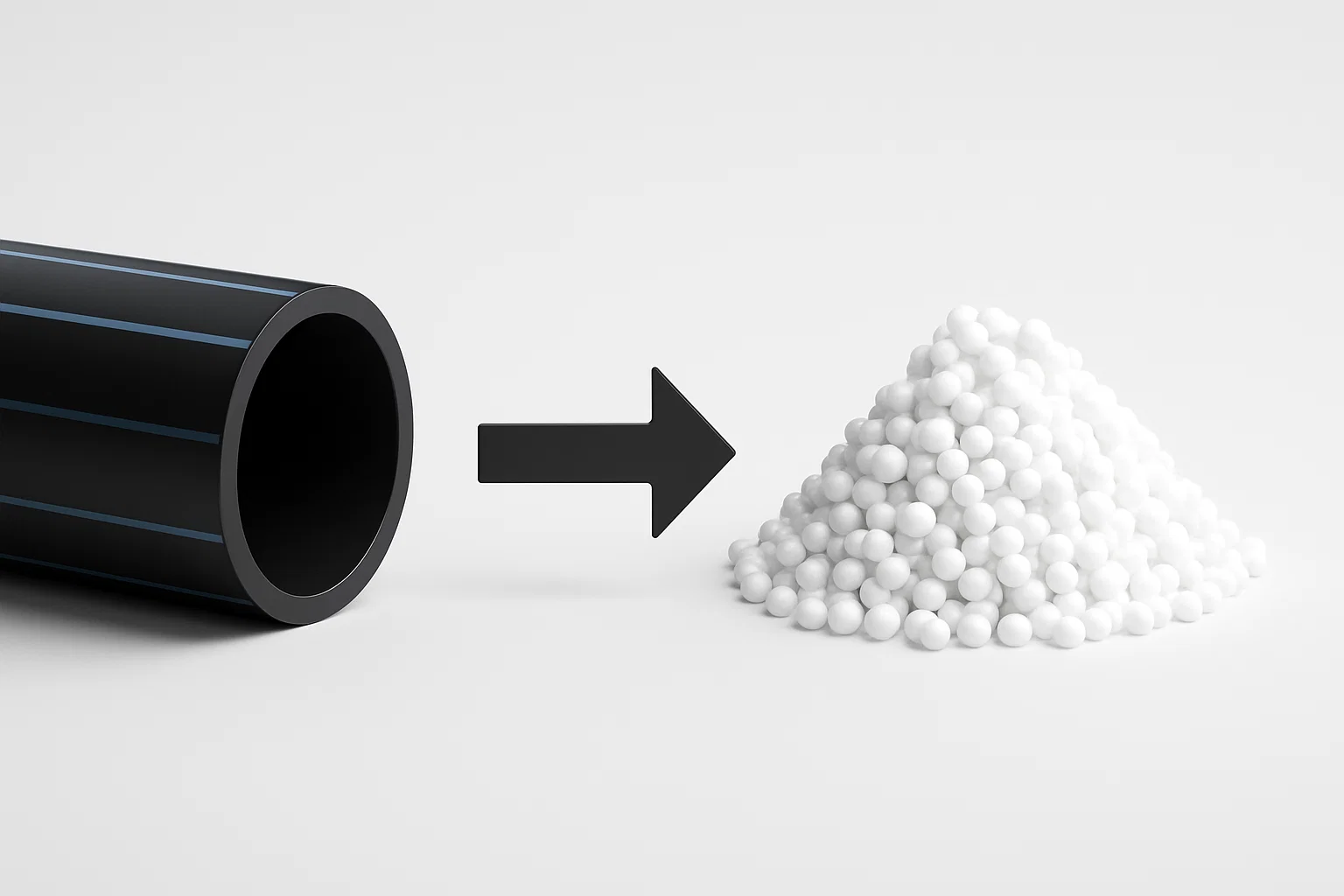
In the world of industrial plastics, High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) stands out for its durability, corrosion resistance, and versatility. It’s the backbone of modern infrastructure, used in everything from municipal water systems and gas distribution to telecommunications conduits. But with millions of tons of HDPE pipes being produced and eventually replaced, a critical question arises: what happens to this valuable material at the end of its life?
The answer lies in a robust and profitable recycling process.
For industrial recycling operators, contractors, and municipal waste managers, discarded HDPE pipes aren’t a liability; they are a valuable resource waiting to be unlocked. This ultimate guide will walk you through the entire HDPE pipe recycling process, step by step, showing you how to turn a bulky waste stream into a high-demand revenue stream.
Chapter 1: The HDPE Pipe Recycling Process: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
Transforming a 50-foot-long, thick-walled pipe into reusable plastic pellets is a multi-stage process. Each step is crucial for ensuring the final product’s quality and market value.
الخطوة 1: التجميع والفرز
The process begins at the source. HDPE pipes are collected from construction sites, infrastructure upgrade projects, and industrial facilities. During this phase, it’s important to sort the pipes, separating HDPE (Plastic #2) from other materials like PVC or metal fittings. While some contamination is inevitable, good initial sorting simplifies the downstream process.
Step 2: Primary Cleaning
Collected pipes are often covered in dirt, mud, or other debris. A preliminary wash removes these surface contaminants, which is vital for protecting the processing equipment in the next stages from excessive wear and tear.
Step 3: Size Reduction – The Critical Shredding Phase
This is the most challenging—and most important—stage in HDPE pipe recycling. Due to their large diameter, long lengths, and tough walls, HDPE pipes cannot be fed directly into a granulator. They must first be broken down into smaller, manageable pieces.
This is where a high-torque, industrial آلة تقطيع أنابيب البولي إيثيلين عالي الكثافة becomes the centerpiece of the operation. Unlike high-speed granulators, a shredder operates at low speed with immense torque, allowing it to:
- Grab and pull in large, bulky pipes without difficulty.
- Shear through thick walls cleanly and efficiently, avoiding jams.
- Handle moderate contamination like residual soil without significant damage to the blades.
The output from the shredder is uniformly sized, coarse plastic chips (typically 40-100mm), which are now perfect for the subsequent processing steps.
Step 4: Secondary Washing and Separation
The shredded HDPE chips undergo a more intensive cleaning process. They are typically fed into a friction washer or a float-sink tank. In a float-sink tank, the HDPE, having a density less than 1 g/cm³, will float, while heavier contaminants like metal fragments, rocks, or other plastics (like PVC) will sink. This is a highly effective purification step.
Step 5: Drying
To prepare for melting, all moisture must be removed from the plastic chips. The clean chips are passed through a thermal or centrifugal dryer until the moisture content is extremely low. Incomplete drying can compromise the quality of the final pellets.
Step 6: Melting and Pelletizing (Extrusion)
The dry, clean HDPE chips are now fed into an extruder. Inside the extruder, they are heated, melted, and homogenized into a consistent molten plastic. This molten plastic is then forced through a die, forming long strands that look like spaghetti. These strands are immediately cooled in a water bath and cut into small pellets by a pelletizer.
These pellets are the final product—a high-quality, recycled raw material ready to be sold and used to manufacture new products.
Chapter 2: Why the Shredder is Your Most Important Investment
For anyone serious about HDPE pipe recycling, the choice of size reduction equipment is paramount. While a granulator is excellent for smaller, brittle plastics, it is ill-suited for the initial processing of large pipes.
Investing in a purpose-built shredder designed for HDPE pipes is not an expense, but a cornerstone investment in operational efficiency. Key features to look for include:
- High-Torque, Low-Speed Motor: Essential for providing the power to process tough materials without the risk of overheating or blockages.
- Robust, Wear-Resistant Blades: The cutting system must be engineered to withstand the abrasive nature of HDPE and potential contaminants.
- Large Feed Opening: The shredder must be able to accommodate the large diameters of the pipes you intend to process.
- Intelligent Control System: Modern shredders feature auto-reverse functions that automatically clear potential jams, ensuring continuous and unmanned operation.
Chapter 3: The Market for Recycled HDPE Pellets
The demand for high-quality recycled HDPE is strong and growing, driven by corporate sustainability goals and government regulations. The pellets you produce can be sold to manufacturers to create a wide range of new products, including:
- New, non-pressurized pipes (e.g., for drainage or agricultural irrigation)
- Composite lumber for decking and outdoor furniture
- Plastic containers, bins, and pallets
- قطع غيار السيارات
- Plastic bags and films
Conclusion: From Challenge to Opportunity
HDPE pipe recycling presents a significant environmental and economic opportunity. What starts as a logistical challenge—disposing of bulky, used pipes—can be transformed into a profitable business line with the right process and the right technology.
The journey from a discarded pipe to a valuable pellet hinges on an efficient, powerful, and reliable size reduction process. By understanding each step and recognizing the central role of a robust HDPE pipe shredder, your operation can effectively tap into this growing market, turning industrial waste into industrial wealth.
Ready to build your recycling operation? Contact our engineering team to discuss the right shredding solution for your specific needs.