Újrahasznosítási hírek
A műanyag újrahasznosítása egyre fontosabbá vált a mai világban, mivel törekedünk egy fenntarthatóbb jövő felé. A műanyag újrahasznosítás egyik kulcsfontosságú eleme a granulálási folyamat, amely során a műanyag darabok granulátumokká válnak, amelyeket új termékek készítésére használnak. Ebben a cikkben a PET darabok újrahasznosítására használt legjobb granulálógépeket fogjuk bemutatni, mélyrehatóan megvizsgálva a piacon elérhető előrehaladott technológiákat és innovatív megoldásokat. A fenntarthatóság ezek a fejlesztések középpontjában áll, biztosítva, hogy a műanyag újrahasznosítás hatékonyabb és környezetbarátabb legyen.
Fejlett műanyag-újrahasznosítási technológiák
Ahogy a műanyag-újrahasznosítás iránti kereslet növekszik, úgy nő az igény a fejlettebb műanyag-újrahasznosítási technológiákra is. Ezek a technológiák az újrahasznosítási folyamat hatékonyságának és eredményességének javítását célozzák, végső soron csökkentve a hulladéklerakókba és az óceánokba kerülő hulladék mennyiségét.
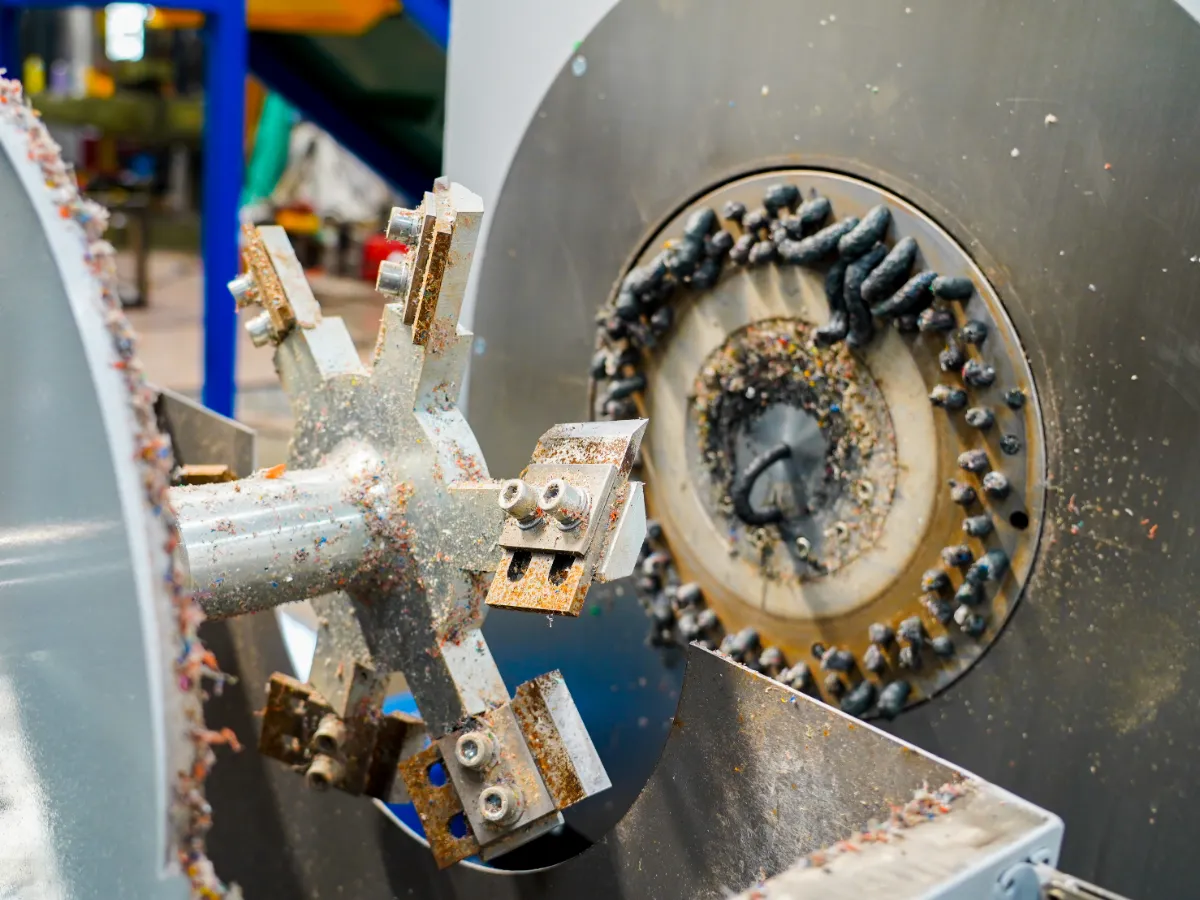
Az egyik ilyen technológia a műanyag pelletizáló gép. Ezek a gépek kulcsszerepet játszanak az újrahasznosítási folyamatban azáltal, hogy a műanyagpelyheket egyenletes pelletekké alakítják, amelyek könnyen felhasználhatók új műanyag termékek gyártásához. Lehetővé teszik a pelletek méretének és alakjának jobb szabályozását, biztosítva a magas minőséget és állandóságot.
De melyek a különböző típusok? műanyag újrahasznosító gépek Elérhető a piacon? Nézzük meg.
Különböző típusú műanyag újrahasznosító gépek
A piacon különféle műanyag-újrahasznosító gépek kaphatók, amelyek mindegyike a különböző újrahasznosítási igényeknek felel meg.
Az egyik népszerű típus a szál pelletizálóEz a gép egy vágórotort használ a műanyag szálak pelletekké vágásához. Hatékony és sokoldalú, így számos műanyag anyaghoz alkalmas. Precíz vágómechanizmusának köszönhetően biztosítja, hogy a pelletek egyenletes méretűek és alakúak legyenek, megfelelve a gyártók szigorú követelményeinek.
Egy másik típus a víz alatti pelletizáló. Ahogy a neve is sugallja, ez a gép víz alatt működik, és olyan egyedi előnyöket kínál, mint a megnövelt hűtési hatékonyság és a csökkentett hulladéktermelés. A víz alatti környezet lehetővé teszi a műanyag gyors lehűlését, ami kiváló fizikai tulajdonságokkal rendelkező pelleteket eredményez. Ez a technológia különösen alkalmas hőérzékeny műanyagok feldolgozására.
Ezenkívül léteznek centrifugális pelletizálók is, amelyek centrifugális erőre támaszkodnak a műanyagpelyhek pelletekké alakításához. Ezek a gépek nagy termelési kapacitásukról és a műanyagok széles skálájának feldolgozására való képességükről ismertek. A gép által generált centrifugális erő biztosítja a műanyag egyenletes eloszlását, ami egyenletes pelleteket eredményez minimális hulladékkal.
Ahogy a műanyag-újrahasznosító ipar folyamatosan fejlődik, a műanyag-újrahasznosítási megoldások innovációi viszik előre az iparágat, hatékonyabbá és fenntarthatóbbá téve az újrahasznosítási folyamatot.
Innovációk a műanyag-újrahasznosítási megoldásokban
A műanyag-újrahasznosítási megoldások innovációi továbbra is előreviszik az iparágat, hatékonyabbá és fenntarthatóbbá téve az újrahasznosítási folyamatot.
A RUMTOO, a műanyag-újrahasznosítás területén vezető vállalat, forradalmasítja az iparágat élvonalbeli megoldásaival. Korszerű műanyag pelletizáló gépek széles választékát kínálják, amelyek a legújabb technológiákat tartalmazzák. Ezeket a gépeket a hatékonyság maximalizálására és a hulladék minimalizálására tervezték, biztosítva, hogy az újrahasznosítási folyamat a lehető legkörnyezetbarátabb legyen.
A RUMTOO innovatív megoldásai közé tartozik, hogy intelligens szenzorokat integrálnak granulálógépeikbe. Ezek a szenzorok különböző paramétereket, mint a hőmérsékletet, a nyomást és a folyási sebességet monitoroznak, lehetővé téve a gyártási folyamat valós idejű finomhangolását. Ez nemcsak a granulátumok minőségét javítja, hanem csökkenti az energiafogyasztást és növeli az általános működési hatékonyságot.
Továbbá, a RUMTOO granulálógépei felszerelve vannak előrehaladott automatizálási funkciókkal, mint például a programozható logikai vezérlők (PLC-k) és az ember-gép interfészek (HMIs). Ezek a funkciók lehetővé teszik az operátorok számára, hogy könnyedén irányítsák és monitorozzák a gépeket, biztosítva a zökkenőmentes működést és a karbantartási idő minimalizálását.
A műanyag-újrahasznosítási technológiák folyamatos fejlődésével és az olyan iparági vezetők elkötelezettségével, mint a RUMTOO, a műanyag-újrahasznosítás jövője ígéretesnek tűnik. Ezen innovatív megoldások alkalmazásával jelentős lépéseket tehetünk egy fenntarthatóbb és környezetbarátabb jövő felé.
Javítsa a műanyag-újrahasznosítási folyamatokat a RUMTOO segítségével
A RUMTOO egy olyan vállalat, amely elkötelezett a műanyag-újrahasznosítási folyamatok forradalmasítása iránt. Korszerű gépeikkel hatékony és fenntartható megoldásokat kínálnak a műanyag-újrahasznosításra.
A műanyag-újrahasznosítást forradalmasító vállalat
A RUMTOO az innováció iránti elkötelezettségével tűnik ki az iparágban. Folyamatosan arra törekszenek, hogy fejlesszék és tökéletesítsék gépeiket, hogy megfeleljenek az újrahasznosító ipar változó igényeinek. Gépeik megbízhatóságukról, hatékonyságukról és kivételes teljesítményükről ismertek.
Korszerű gépek a hatékony újrahasznosításhoz
A RUMTOO számos élvonalbeli műanyag pelletizáló gépet kínál, amelyeket az újrahasznosítási folyamatok fokozására terveztek. Ezek a gépek olyan fejlett funkciókkal vannak felszerelve, mint a nagy sebességű rotorok, a hőmérséklet-szabályozó rendszerek és a precíziós vágási technológia.
Az egyik figyelemre méltó gép a RUMTOO-2000, amely nagy mennyiségű műanyagpelyhet képes feldolgozni és kiváló minőségű pelletekké alakítani. Innovatív kialakítása minimális energiafogyasztást és csökkentett hulladéktermelést biztosít.
A RUMTOO által kínált másik gép a RUMTOO-500, amely ideális kisebb volumenű újrahasznosítási műveletekhez. Kompakt mérete ellenére kiváló teljesítményt és hatékonyságot biztosít, így értékes eszköz minden méretű vállalkozás számára.
Fenntartható megoldások a műanyag-újrahasznosításhoz
A fejlett géppark mellett a RUMTOO megoldásaiban a fenntarthatóságot is előtérbe helyezi. Felismerik a műanyag-újrahasznosítás környezeti hatásainak minimalizálásának fontosságát, és hatékony és környezetbarát folyamatok létrehozására törekszenek.
Ennek egyik módja az energiahatékony alkatrészek és rendszerek használata. Gépeiket úgy tervezték, hogy kevesebb energiát fogyasztsanak, csökkentve az újrahasznosítási folyamat szénlábnyomát. Ezenkívül a RUMTOO gépek a legmodernebb szűrőrendszerekkel rendelkeznek, amelyek biztosítják, hogy a folyamat során keletkező kibocsátásokat és hulladékot megfelelően kezeljék és minimalizálják.
A RUMTOO fenntarthatósági elkötelezettsége azonban ennél nem áll meg. Aktívan együttműködnek kutatóintézetekkel és iparági szakértőkkel, hogy új módszereket keressenek ki a műanyag újrahasznosítás javítására. A technológiai előrehaladások és iparági trendek élén tartása révén a RUMTOO folyamatosan innovál és korszerű megoldásokat kínál.
Továbbá a RUMTOO elkötelezett a műanyag-újrahasznosítás fontosságával kapcsolatos oktatás és tudatosság növelése iránt. Workshopokat és képzési programokat szerveznek, hogy felvértezze az egyéneket és a vállalkozásokat a hatékony újrahasznosítási gyakorlatok megvalósításához szükséges ismeretekkel és készségekkel.
Összefoglalva, a műanyag pelletizáló gépek létfontosságú szerepet játszanak a PET-pehely újrahasznosításában. A RUMTOO-hoz hasonló vállalatok által kínált fejlett technológiák és innovatív megoldások viszik előre az iparágat, hatékonyabbá és fenntarthatóbbá téve az újrahasznosítási folyamatot. Élvonalbeli kialakításukkal és a fenntarthatóság iránti elkötelezettségükkel ezek a gépek egy zöldebb jövő felé nyitják az utat. A csúcskategóriás műanyag pelletizáló gépekbe való befektetéssel a vállalkozások hozzájárulhatnak a körforgásos gazdasághoz, és segíthetnek egy olyan világ megteremtésében, ahol a műanyaghulladék a múlté.
A műanyag pelletizáló gépek kulcsfontosságúak a műanyagiparban, mivel a nyers műanyagokat pelletekké alakítják, amelyek különféle termékek gyártásához használhatók. Ha fontolgatja a befektetést, fontos megérteni azokat a tényezőket, amelyek befolyásolják a költségüket. Ez a cikk a műanyag pelletizáló gépek árképzését befolyásoló kulcsfontosságú elemeket vizsgálja, beleértve a gép specifikációit, a termelési kapacitást és a márka hírnevét.
Műanyag pelletizáló gép vásárlásakor a potenciális vásárlók gyakran számos lehetőséggel szembesülnek, a költségvetésbarát modellektől a csúcskategóriás opciókig. Ez az útmutató részletes áttekintést nyújt a piacon elérhető különböző modellekről, kiemelve azok tulajdonságait, előnyeit és árpontjait, hogy segítsen megalapozott döntést hozni.
A műanyag granulátorok kulcsszerepet játszanak a műanyag-újrahasznosítási folyamatban, mivel a műanyaghulladékot apró, egyenletes granulátumokká alakítják, amelyeket új műanyag termékek gyártásához lehet felhasználni. Annak érdekében, hogy a műanyag granulátor csúcshatékonyan működjön és hosszú élettartammal rendelkezzen, elengedhetetlen egy szigorú karbantartási rutin bevezetése és a problémák azonnali kezelése.