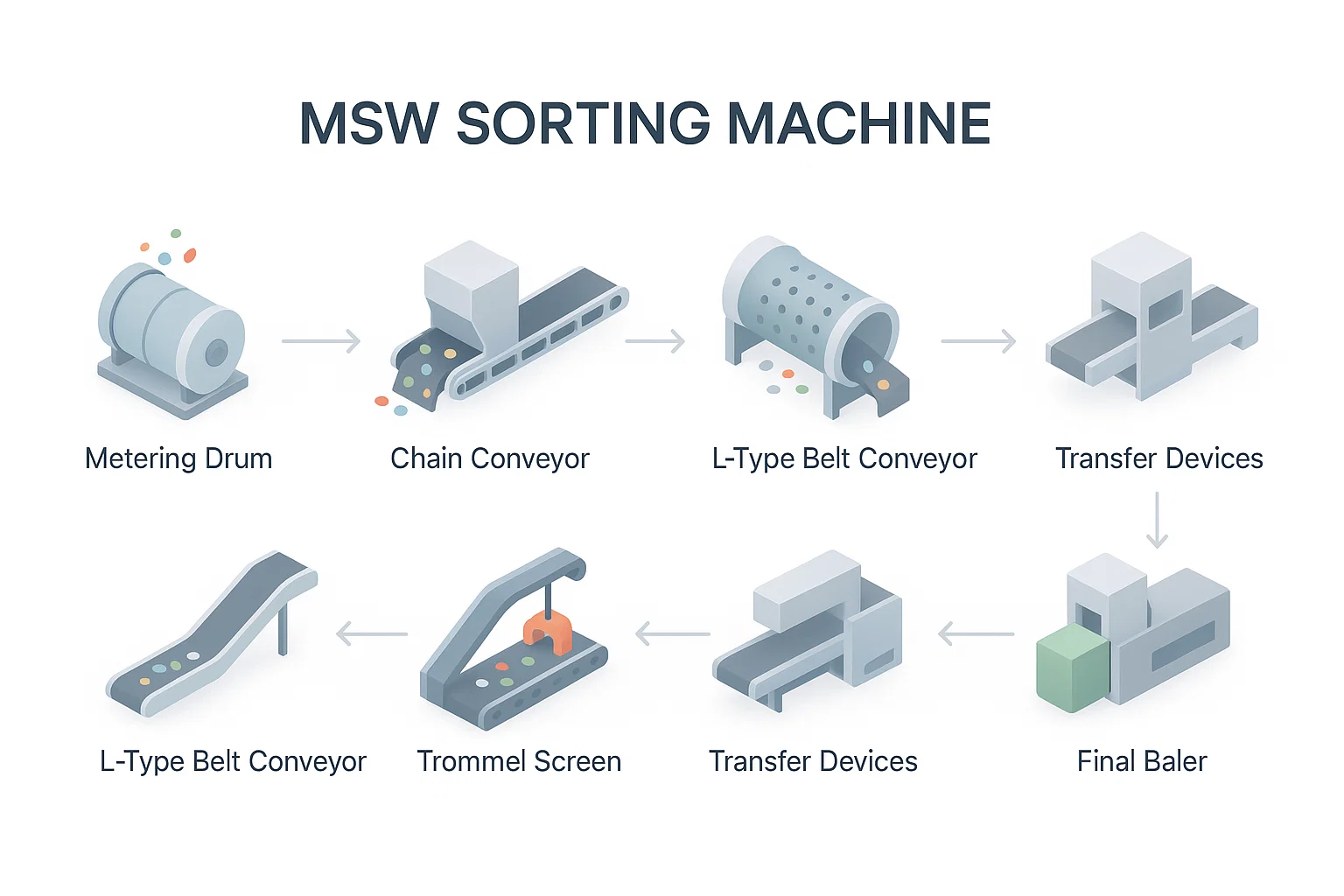
System sortowania MSW (Municipal Solid Waste) to wyrafinowany, wieloetapowy zakład zaprojektowany do wydajnego przetwarzania i oddzielania odpadów domowych na wartościowe frakcje nadające się do recyklingu i jednorazowe. Diagram przedstawia szczegółowy układ systemu, podkreślając każdy etap procesu sortowania i kluczowe maszyny w nim uczestniczące.
Kluczowe komponenty i przepływ procesu
- Bęben dozujący:
Proces rozpoczyna się od bębna dozującego, który reguluje przepływ przychodzących odpadów, zapewniając stałą szybkość podawania do systemu. Ten krok jest kluczowy dla utrzymania optymalnej wydajności operacyjnej i zapobiegania przeciążeniom systemu. - Przenośnik łańcuchowy:
Odmierzone odpady są następnie transportowane za pomocą solidnego przenośnika łańcuchowego. Przenośnik ten jest przeznaczony do obsługi mieszanych strumieni odpadów i podnoszenia materiału do następnego etapu przetwarzania. - Rozbijacz worków:
Na tym etapie rozrywacz worków rozrywa plastikowe worki, uwalniając ich zawartość i umożliwiając skuteczniejsze sortowanie w dół. To działanie mechaniczne jest niezbędne do odsłonięcia materiałów nadających się do recyklingu i materii organicznej, które w przeciwnym razie pozostałyby uwięzione. - Przenośnik taśmowy typu L:
Rozbite odpady są przenoszone na przenośnik taśmowy typu L, który przesuwa materiał do bębna. Konstrukcja w kształcie litery L umożliwia zmiany wysokości i kierunku w układzie obiektu. - Bęben:
Bęben to obracający się cylindryczny ekran, który oddziela odpady na podstawie ich wielkości. Mniejsze cząstki, takie jak materia organiczna i drobne zanieczyszczenia, spadają przez ekran, podczas gdy większe przedmioty są przenoszone dalej w celu dalszego sortowania. - Separator magnetyczny:
Jak wskazano na widoku z góry, separator magnetyczny jest zintegrowany z linią w celu ekstrakcji metali żelaznych ze strumienia odpadów. Ten krok jest niezbędny do odzyskiwania cennych metali i zapobiegania zanieczyszczeniu innych frakcji nadających się do recyklingu. - Urządzenie transferowe i dodatkowe przenośniki:
Po przesianiu i separacji magnetycznej materiał przechodzi przez dodatkowe przenośniki taśmowe typu L i urządzenie transferowe, które pomagają rozprowadzać i kierować różne frakcje odpadów do odpowiednich miejsc docelowych. - Taśmociąg i prasa:
Ostatni etap obejmuje przenośnik taśmowy, który dostarcza posortowane materiały nadające się do recyklingu do prasy. Prasa zagęszcza te materiały w gęste, łatwe do opanowania bele do przechowywania, transportu lub sprzedaży do zakładów recyklingu.
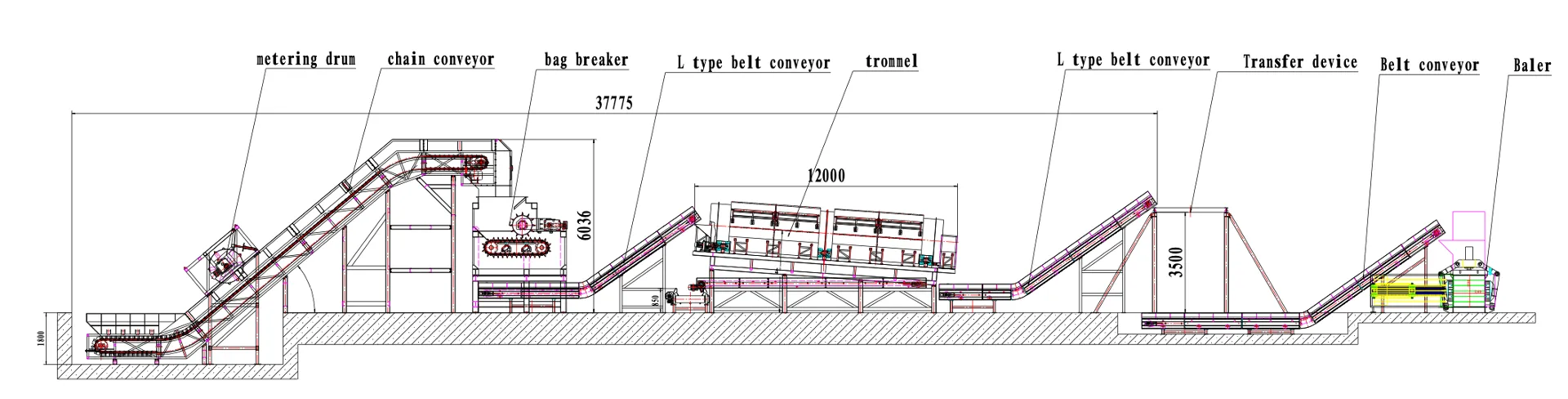
Układ i wydajność systemu
System jest zaprojektowany do integracji pionowej i poziomej, jak pokazano na widokach z boku i z góry. Kluczowe wymiary (np. całkowita długość linii 51 411 mm, zmiany wysokości 6036 mm i 3500 mm) wskazują na dużą skalę, przemysłową operację zdolną do przetwarzania dużych ilości odpadów komunalnych.
Wniosek
System sortowania MSW przedstawiony na schemacie jest przykładem nowoczesnej technologii gospodarowania odpadami, łączącej metody mechaniczne, magnetyczne i oparte na przenośnikach, aby zmaksymalizować odzysk i zminimalizować składowanie na wysypiskach. Każdy komponent odgrywa określoną rolę w usprawnianiu procesu sortowania, poprawianiu wskaźników recyklingu i wspieraniu zrównoważonych praktyk gospodarowania odpadami.