Uništavač tvrdih diskova: Razine sigurnosti i kontrolni popis specifikacija (2026.)
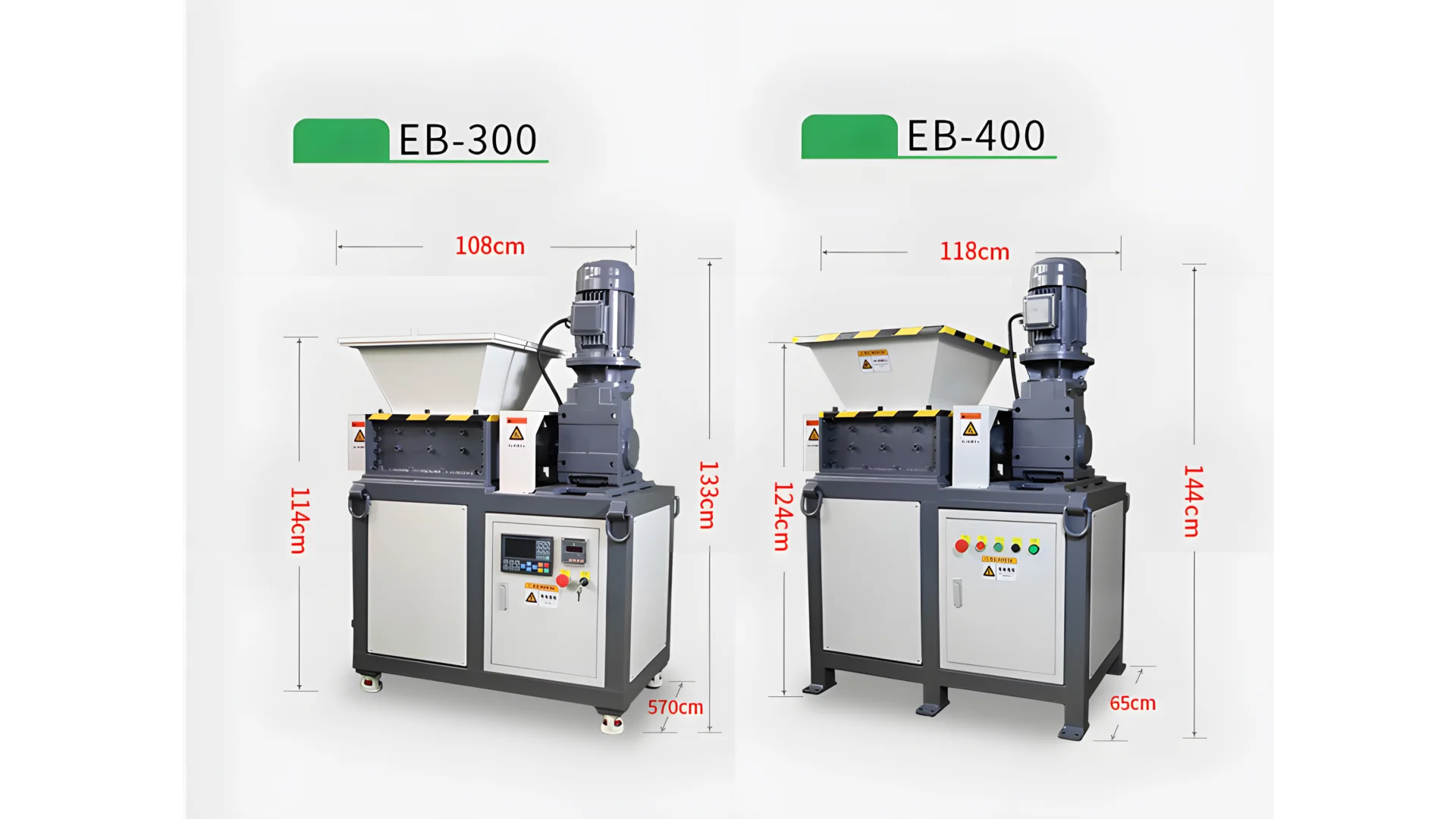

Kada povrede podataka mogu koštati milijune u kaznama i štetiti ugledu, brisanje softvera može biti nedovoljno za neke modele prijetnji. Fizičko uništavanje je široko rasprostranjeno...