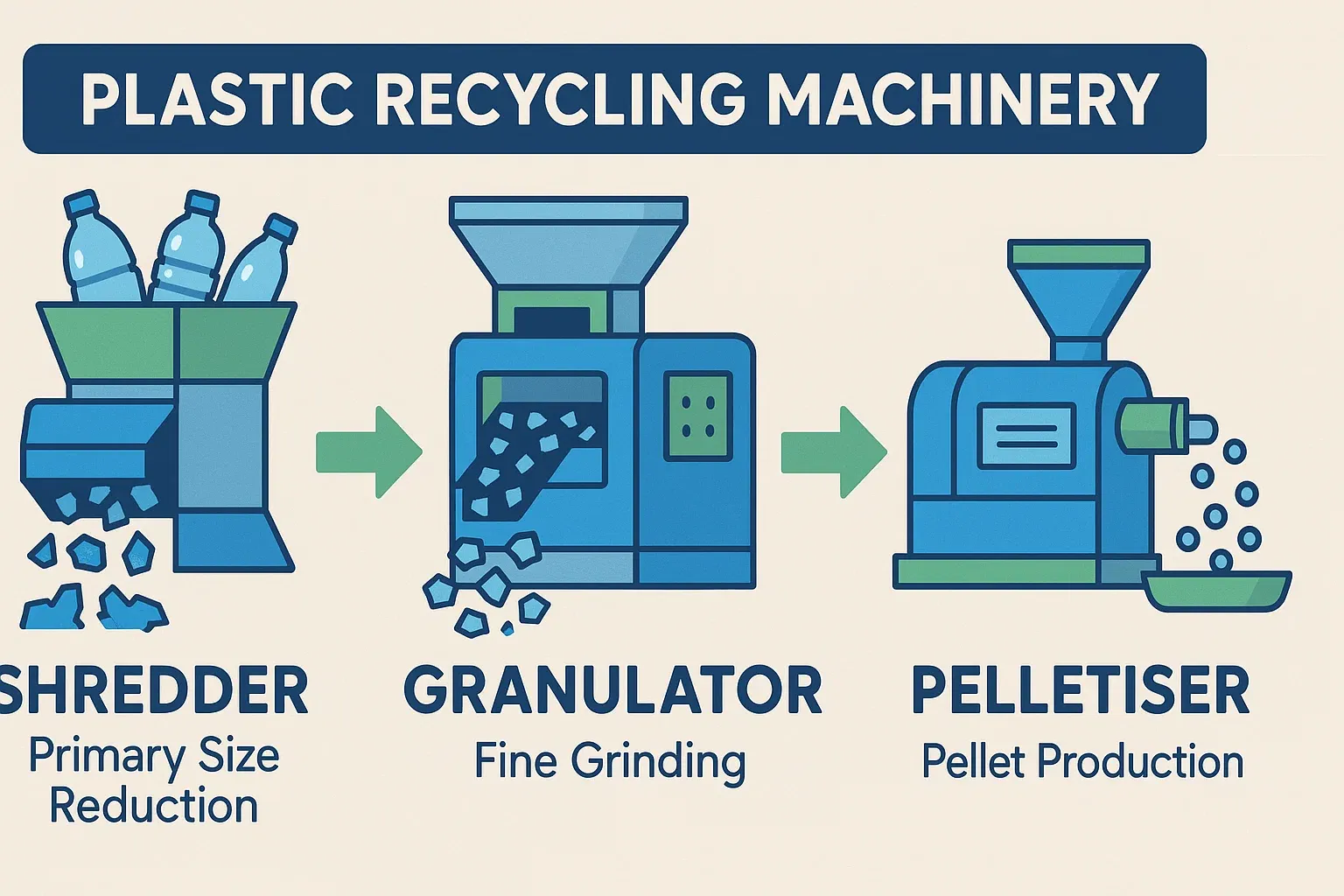
분쇄기 vs. 분쇄기 vs. 펠렛화기: 차이점과 시너지 효과 이해
플라스틱 재활용 분야에서 과립기, 분쇄기, 펠렛화기는 공통적이지만 기능적으로는 서로 다른 세 가지 장비입니다. 재활용 공정을 최적화하기 위해서는 이들 장비의 차이점과 상호 연결을 명확하게 이해하는 것이 중요합니다.
분쇄기
파쇄기는 주로 크고 부피가 크거나 혼합된 플라스틱 폐기물의 초기 크기 감소에 사용됩니다. 일반적으로 찢기, 전단 또는 충격 방식을 사용하여 더 크고 불규칙한 크기의 조각을 생산합니다. 파쇄기는 특히 부피가 너무 크거나 파쇄기 호퍼에 직접 투입하기 어려운 물질을 처리할 때 과립기의 전처리 장비로 사용되는 경우가 많습니다. 파쇄기의 주요 목표는 최종 입자의 균일성을 덜 중시하면서, 이후 처리를 용이하게 하기 위해 물질의 부피를 줄이는 것입니다.
과립기
이름에서 알 수 있듯이 과립기는 고속 회전 블레이드를 사용하여 플라스틱을 미세하게 절단하고 분쇄하여 더 작고 비교적 균일한 입자 또는 플레이크(종종 재생재라고 함)를 생성합니다. 이 재생재는 제조 과정에 직접 재사용되거나 펠렛화기의 원료로 사용될 수 있습니다.
펠렛화기
펠렛타이저는 일반적으로 재활용 라인의 마지막에 위치합니다. 세척 및 파쇄된 (과립 상태일 수도 있음) 플라스틱을 용융하여 다이 헤드를 통해 스트랜드 형태로 압출합니다. 이 스트랜드들은 펠렛화 장치(예: 워터링, 공랭식, 수중식)를 통해 균일하고 시장성 있는 플라스틱 펠렛으로 절단됩니다. 이렇게 절단된 펠렛은 모양, 크기, 겉보기 밀도가 일정하여 보관, 운반 및 후속 플라스틱 성형 공정에서 사용하기가 용이합니다.
재활용 라인의 시너지
이 세 가지 유형의 장비는 재활용 라인에서 시너지 효과를 발휘할 수 있습니다. 일반적인 공정은 다음과 같습니다. 대형 폐기물은 먼저 파쇄기로 들어가 조분쇄된 후, 과립기로 이송되어 미세 분쇄됩니다. 세척 및 건조 후 생성된 재분쇄물은 펠렛화기로 이송되어 용융, 압출, 최종 플라스틱 펠렛으로 절단됩니다. 일부 통합 시스템은 파쇄, 공급, 압출(펠렛화) 기능을 단일 단계로 결합하기도 합니다.
최적의 재활용 라인 구성(예: 파쇄기 → 과립기 → 펠렛타이저 vs. 과립기 → 펠렛타이저)은 투입 재료의 형태와 용량, 그리고 최종 제품에 필요한 사양에 따라 크게 달라집니다. 단 하나의 "최적" 순서는 없습니다. 장비 선택 및 순서는 재료 특성과 처리 목표에 따른 전략적 결정이며, 재활용 라인을 설계하는 엔지니어에게 매우 중요합니다.
장비 역할 오해의 결과
파쇄기, 과립기, 펠렛화기의 각기 다른 역할을 혼동하면 처리 효율이 떨어지고, 에너지 소비가 증가하며, 재활용 재료의 품질이 저하되어 궁극적으로 투자 수익률에 부정적인 영향을 미칠 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, 파쇄기에 더 적합한 매우 크거나 질긴 재료를 처리하기 위해 과립기를 사용하면 칼날과 스크린의 과도한 마모, 잦은 막힘, 그리고 모터 과부하가 발생할 수 있습니다. 마찬가지로, 과립화된 재분쇄물이 펠렛화된 과립과 동일한 물리적 특성을 가질 것이라고 기대하는 것은 비현실적입니다. 이러한 장비의 기능을 명확하게 구분하면 구매자가 정보에 기반한 투자 결정을 내리고 엔지니어가 효율적인 재활용 시스템을 설계할 수 있도록 도와줍니다.