Recycling News
In the world of PET recycling, PVC (polyvinyl chloride) is a dreaded contaminant. Even in trace amounts, PVC can wreak havoc during the processing and remanufacturing of post-consumer PET resin, leading to significant quality issues in the final product. For context, PVC contamination as low as 50 parts per million (ppm)—equivalent to just 0.05 kg of PVC in 1,000 kg of PET flakes—can cause severe problems. This minuscule concentration (0.005%) can lead to the breakdown of PET resin, resulting in brittleness, discoloration (yellowing), and the release of hazardous chlorine vapors. These issues undermine two of PET's most valued properties: clarity and impact strength.
Plastic film recycling is an essential aspect of modern waste management, addressing the growing challenge of managing lightweight, flexible plastic waste. This survey note provides an in-depth exploration of film recycler machines, their features, benefits, and operational mechanisms, drawing on extensive research to ensure a thorough understanding for both industry professionals and lay readers.
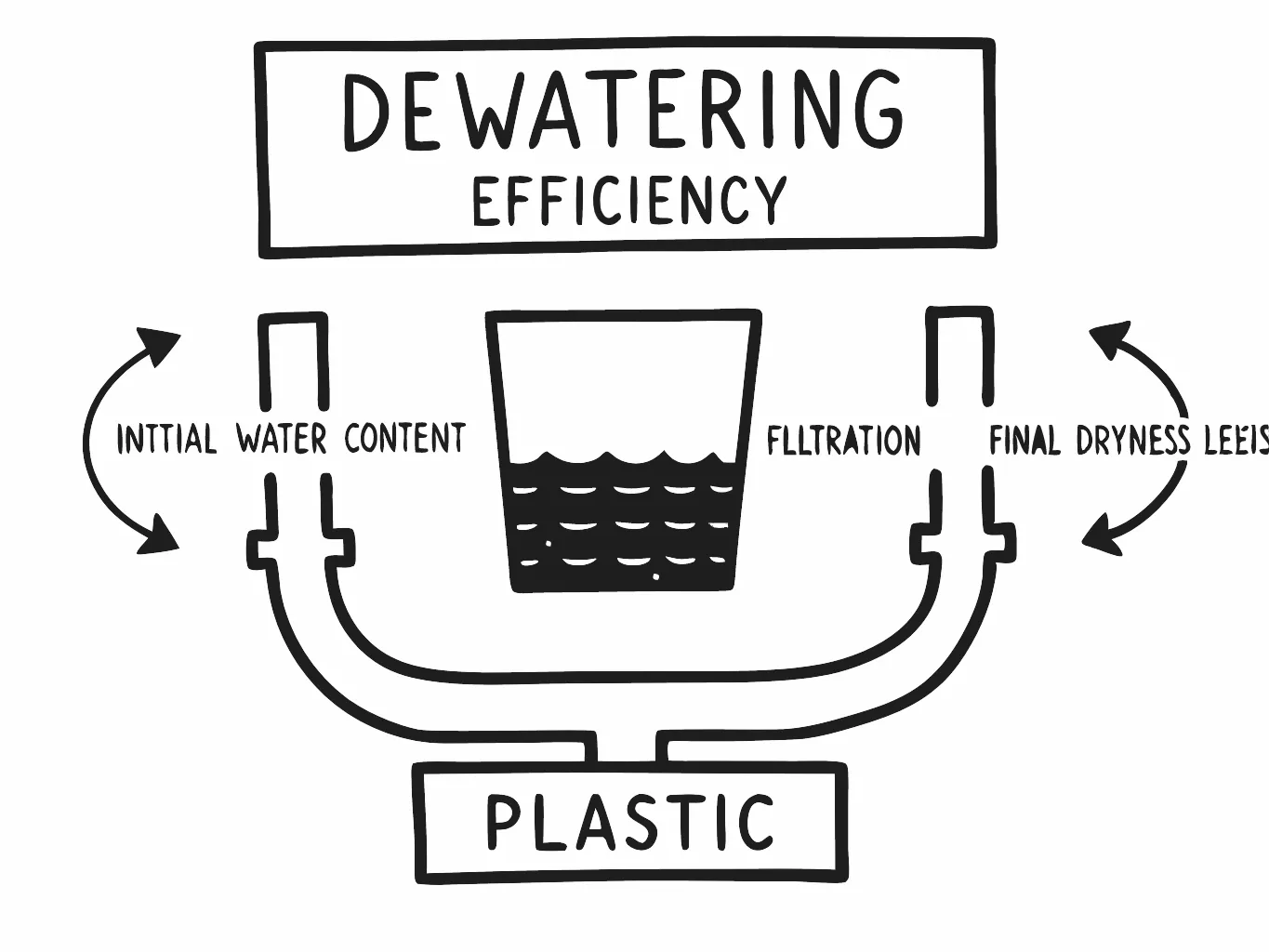
When it comes to maximizing dewatering efficiency for plastic films—think polyethylene (PE) or polypropylene (PP)—the equipment you choose can make or break your recycling operation. These machines aren’t just tools; they’re investments in quality output, cost savings, and sustainability. Let’s break down the standout features, benefits, and qualities of mechanical dewatering equipment, focusing on what matters most to businesses in this space.
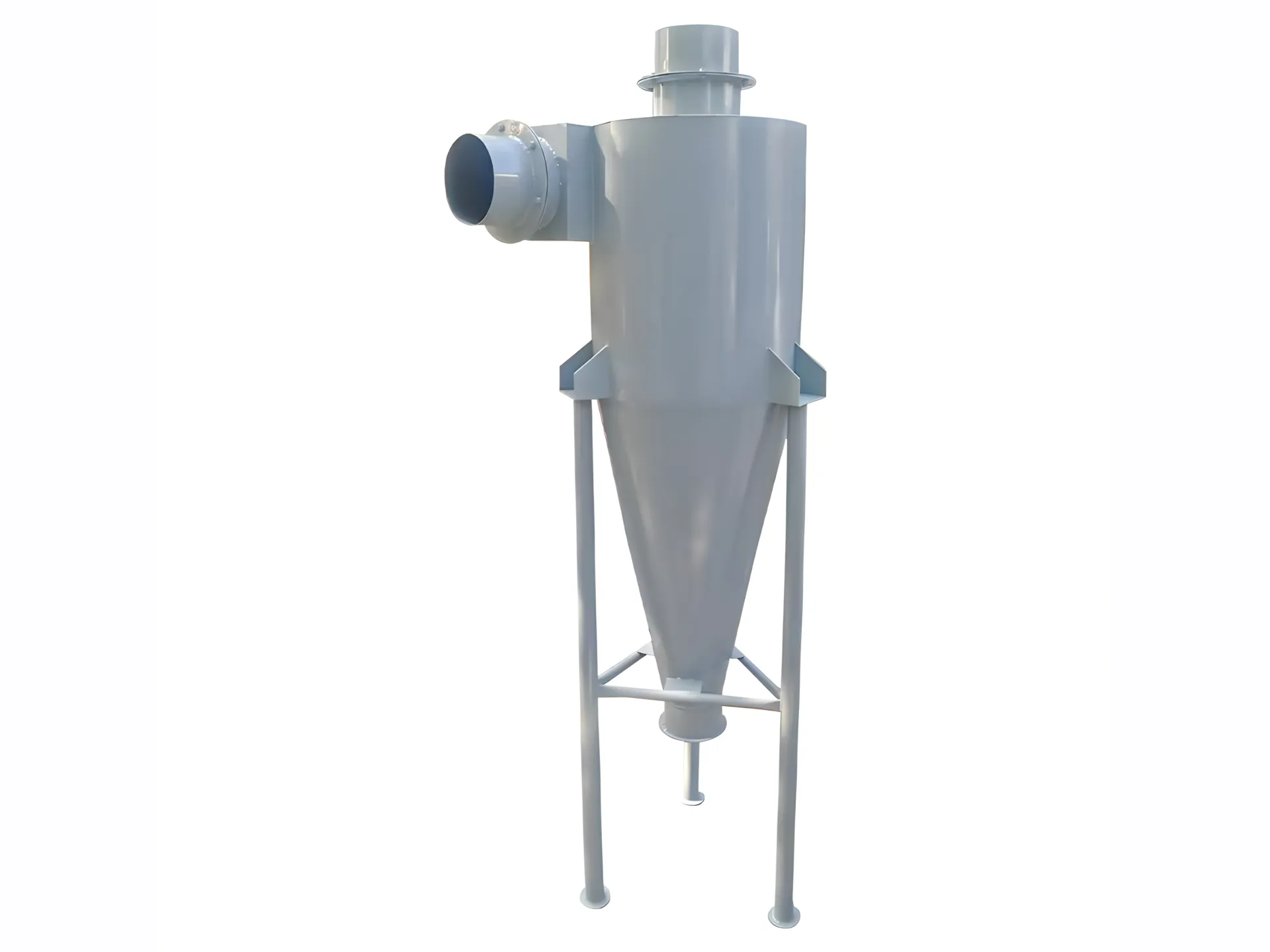
Cyclone Separators in Plastic Recycling: Key Mechanisms & Applications
Cyclone separators are critical in plastic recycling for efficiently sorting and purifying materials by leveraging differences in particle density, size, and airflow dynamics. Here’s how they are tailored to meet industry-specific needs:
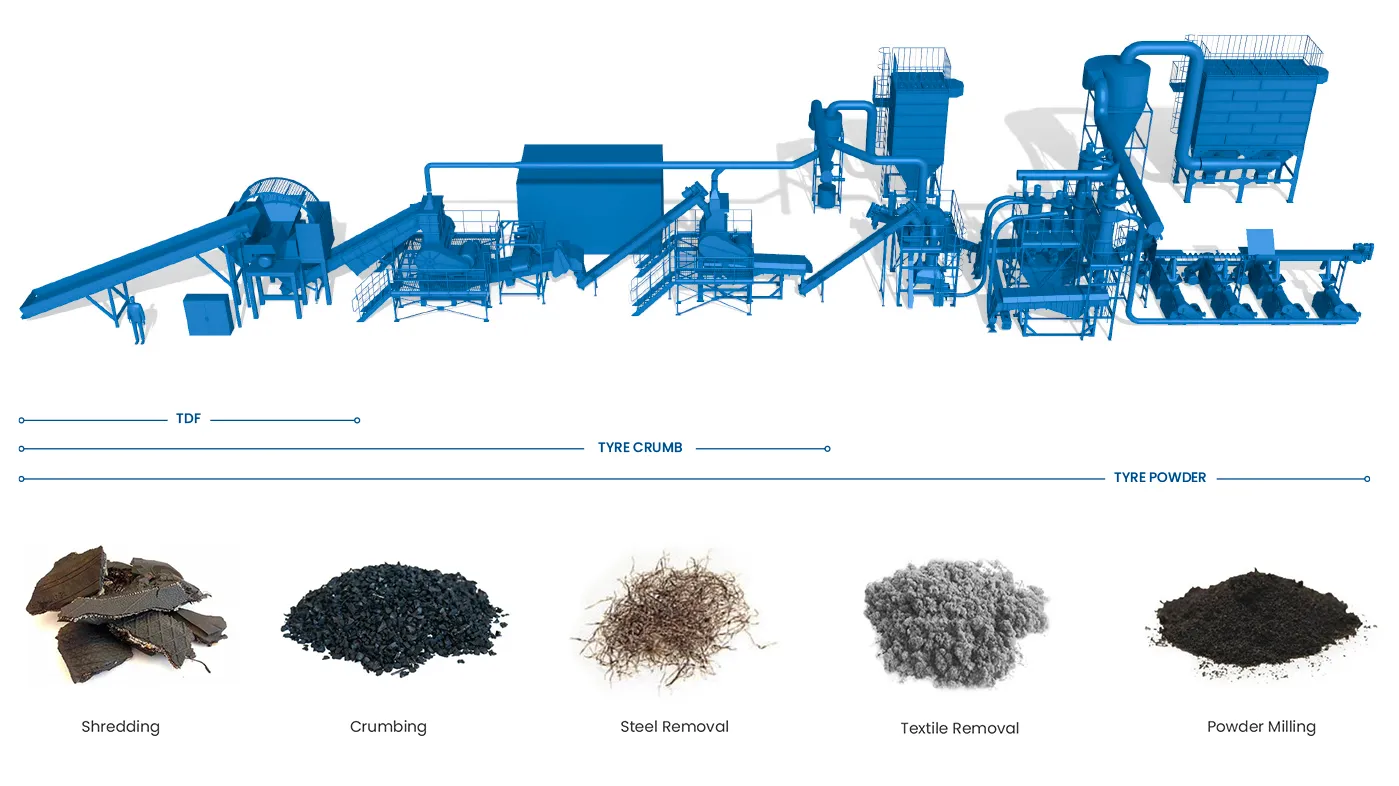
Tire recycling is an essential process in managing the increasing volume of discarded tires. A critical step in this process involves cutting the sidewall of the tire. Understanding the rationale behind this step highlights its significance in the recycling chain and its impact on material recovery and equipment efficiency.
For small businesses, selecting the right plastic recycling equipment requires balancing cost, efficiency, and long-term operational needs. Here are practical suggestions from the perspectives of core functions, applicable scenarios, and cost-effectiveness.
Tire recycling plays a pivotal role in addressing the global environmental crisis caused by the disposal of millions of used tires annually. With over 56 million tires processed each year in many countries, establishing effective tire recycling systems is essential for sustainable waste management and environmental preservation.
Addressing the global challenge of plastic waste, polyethylene terephthalate (PET) stands out due to its widespread applications and recyclability. Efficient PET recycling systems are crucial for realizing a circular economy and reducing reliance on virgin resources. This article provides a professional overview of the core components of a PET recycling machine, elucidating how these essential modules work in concert to transform post-consumer PET materials into high-quality recycled feedstocks. We will delve into the equipment configurations of critical stages including pre-processing, washing, sorting, and extrusion pelletizing, briefly analyzing the technical specifications and performance metrics of each section. This aims to offer industry professionals a deeper understanding of the PET recycling process flow and equipment composition.
Environmental awareness is growing, making the recycling of PET bottles more critical than ever. PET washing lines are designed to handle post-consumer bottles with caps and labels, transforming them into high-purity, low-moisture PET flakes. This process ensures a more sustainable future by improving recycling efficiency.
What is PET Recycling and Why is it Important?
Polyethylene Terephthalate, commonly known as PET, is a type of plastic used extensively in packaging, particularly for beverages and food products. Recycling PET is vital for reducing plastic waste, conserving resources, and mitigating environmental impact. With increasing global awareness and regulatory pressure to move towards a circular economy, the demand for effective PET recycling solutions is on the rise.
Choosing the right PET recycling machine is a critical decision for businesses in the recycling industry. The right machine can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and ensure high-quality output. However, with so many options available, it can be challenging to determine which machine best fits your needs. This guide provides a comparative analysis of PET recycling machines to help you make an informed decision.