Recycling News
Understanding Sorting Machinery in Plastic Recycling
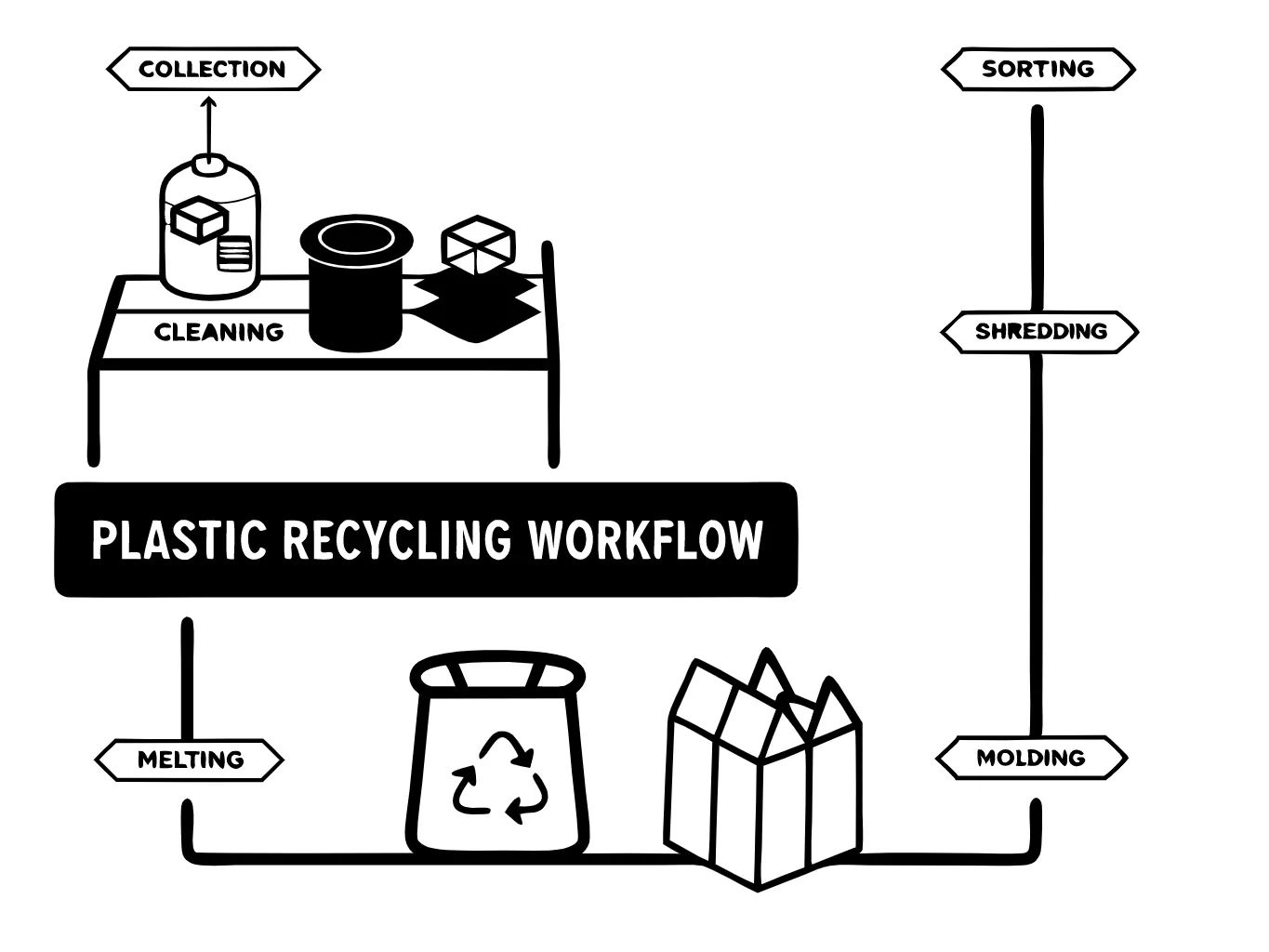
Sorting machinery in the plastic recycling industry plays a crucial role in classifying different types of plastic materials based on attributes such as color, density, and composition. These machines simplify the sorting process through advanced technologies and processes, ensuring optimal material recovery efficiency.
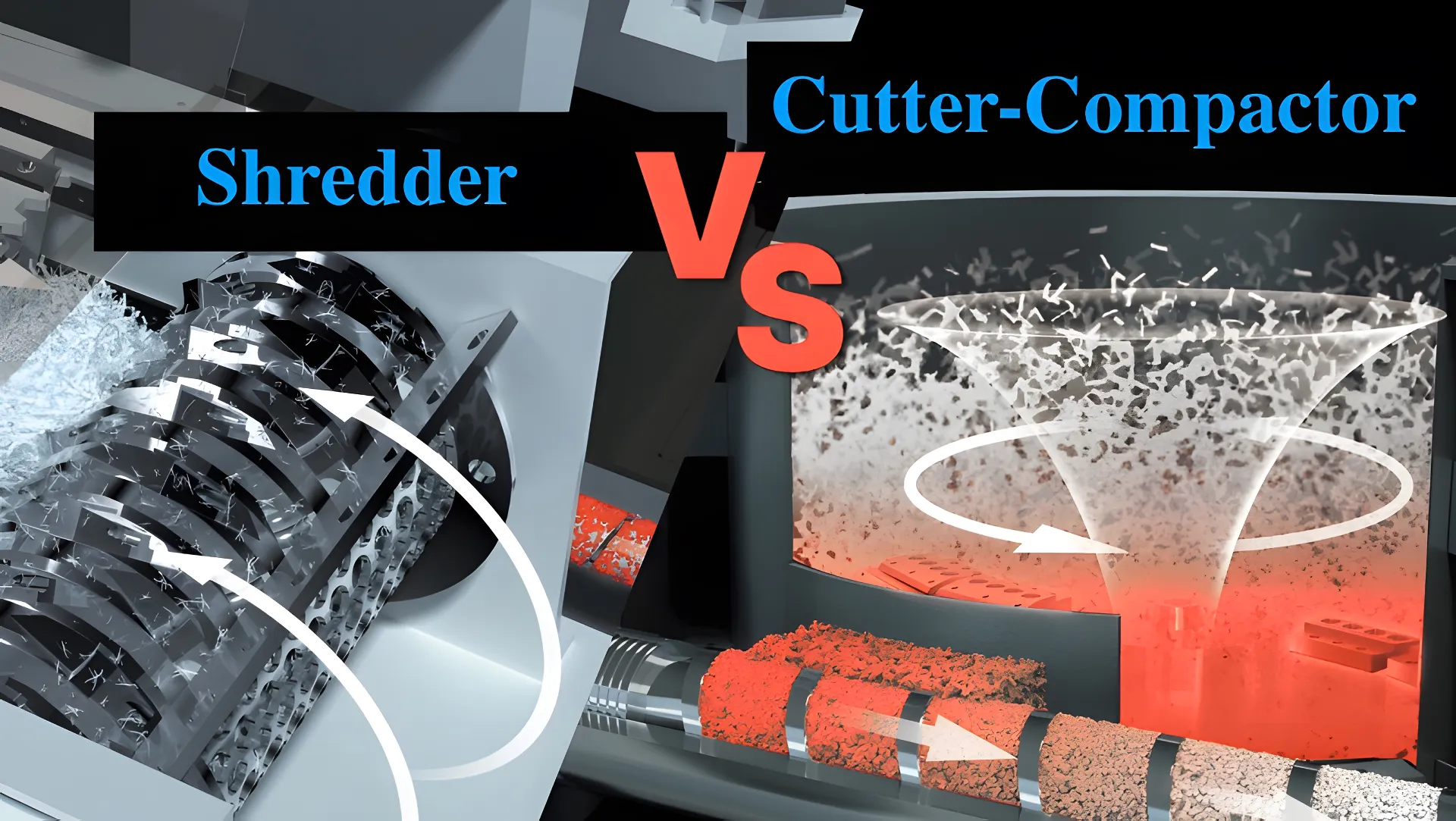
The right plastic recycling machine is crucial for improving operational efficiency. Both cutter-compactors and shredders can effectively reduce the size of plastic waste, but they work in different ways. This article will help you determine which machine is best suited for your recycling needs.
Understanding Cutter-Compactors and Shredders in Plastic Recycling
When selecting equipment for plastic recycling, it's important to understand the differences between cutter-compactors and shredders. These two machines play distinct roles in preparing plastic waste for extrusion and pelletizing. This article explores the key differences in their functions, applications, and material suitability.
How Does Customization Maximize Efficiency in Plastic Recycling?
Customizing plastic recycling machines is crucial for enhancing the efficiency of recycling operations. Here's how customization can transform your recycling process:
Today, plastic products come in various shapes, sizes, layers, print levels, and formulations, making the recycling process challenging. Selecting the right plastic recycling line, feeding system, degassing system, filtration device, and pelletizing system can significantly improve recycling efficiency. Therefore, the first step in choosing recycling equipment is to accurately identify the type of plastic waste.
Plastic recycling is a critical part of reducing waste and conserving resources. However, not all plastic waste is created equal. Two primary types of plastic recycling are Post-Industrial and Post-Consumer. While both aim to recycle plastic and reduce landfill waste, they operate under different conditions and processes. In this article, we’ll explore the distinctions between these two recycling methods and their unique advantages.
Polystyrene, commonly found in products like foam cups, take-out containers, packaging materials, and disposable cutlery, is one of the most widely used yet environmentally problematic plastics in the world. Though convenient for consumers, the impact of polystyrene on our environment has been significant, especially since it’s non-biodegradable and accumulates in landfills and oceans. Recycling polystyrene, however, offers an effective solution to mitigate these environmental concerns.
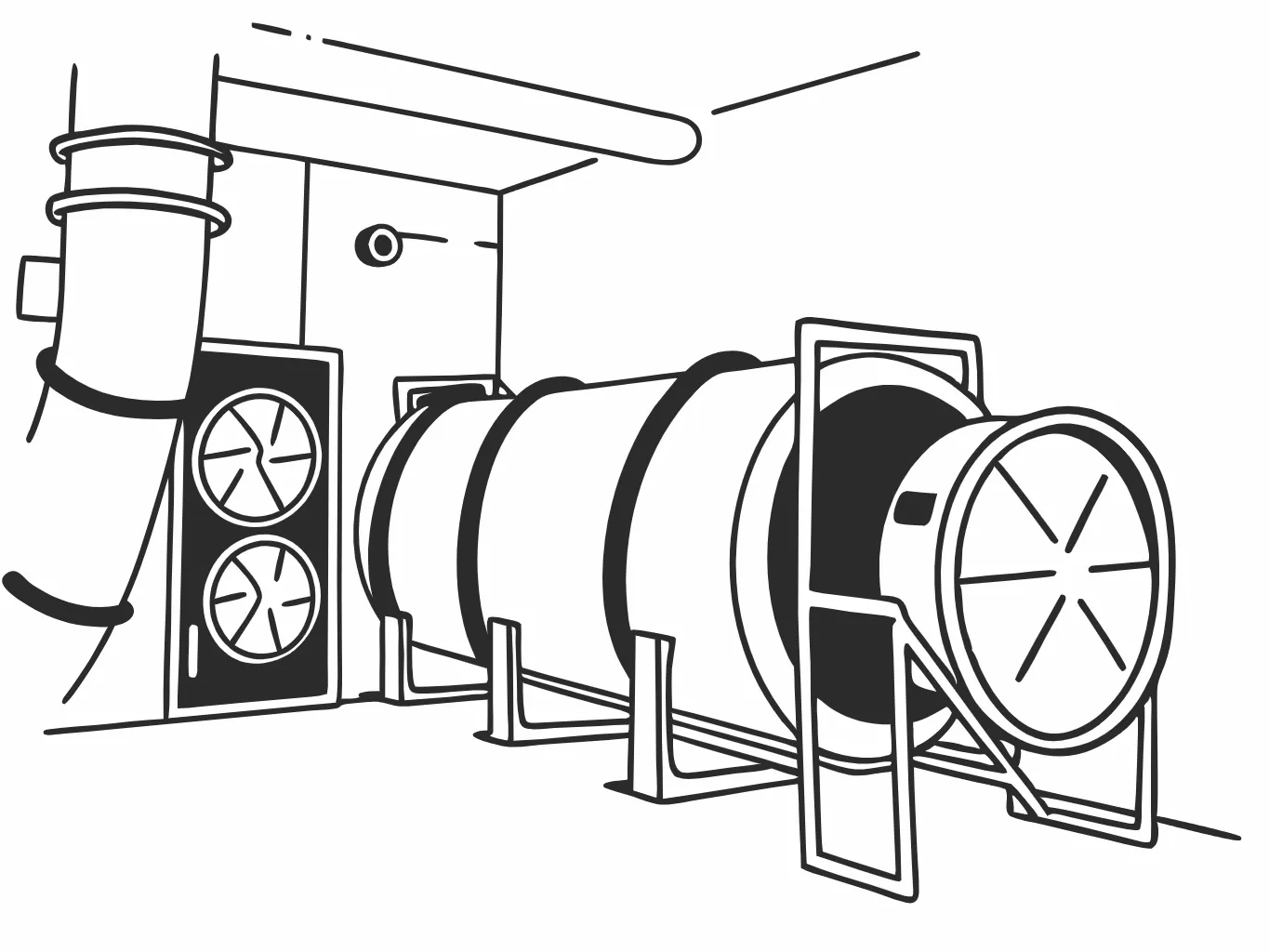
What Are Centrifugal Dryers?
Centrifugal dryers are specialized machines used in the plastic recycling industry to separate and dry plastic materials. They leverage the power of centrifugal force to remove moisture from plastic granules or flakes after washing processes, ensuring that the recycled plastic is dry enough for further processing or melting.
Centrifugal dryers play a critical role in plastic recycling by efficiently removing moisture from plastic pellets, flakes, or regrind. Proper maintenance and care are essential to ensure these machines operate at peak performance and last for years. Neglecting maintenance can lead to costly repairs, downtime, and reduced efficiency. Below, we outline practical tips to help you maximize the lifespan of your centrifugal dryer.
Integrating a centrifugal dryer into your plastic recycling workflow can significantly improve efficiency, reduce drying time, and lower energy costs. Centrifugal dryers are essential for removing moisture from plastic pellets, flakes, or regrind after washing. To maximize their benefits, you need a clear strategy for installation, operation, and maintenance. This guide explains how to seamlessly incorporate a centrifugal dryer into your recycling process.
In industrial drying processes, choosing the right method can significantly impact energy consumption and operational efficiency. Two common drying methods are mechanical centrifugal drying and air drying. Understanding the energy input required for each can help businesses make informed decisions that optimize both cost and performance.
Centrifugal dryers play a crucial role in improving the efficiency of plastic recycling operations. These machines are designed to remove excess moisture, contaminants, and residues from plastic materials, enhancing the quality of recycled plastic and increasing the overall productivity of the recycling process.