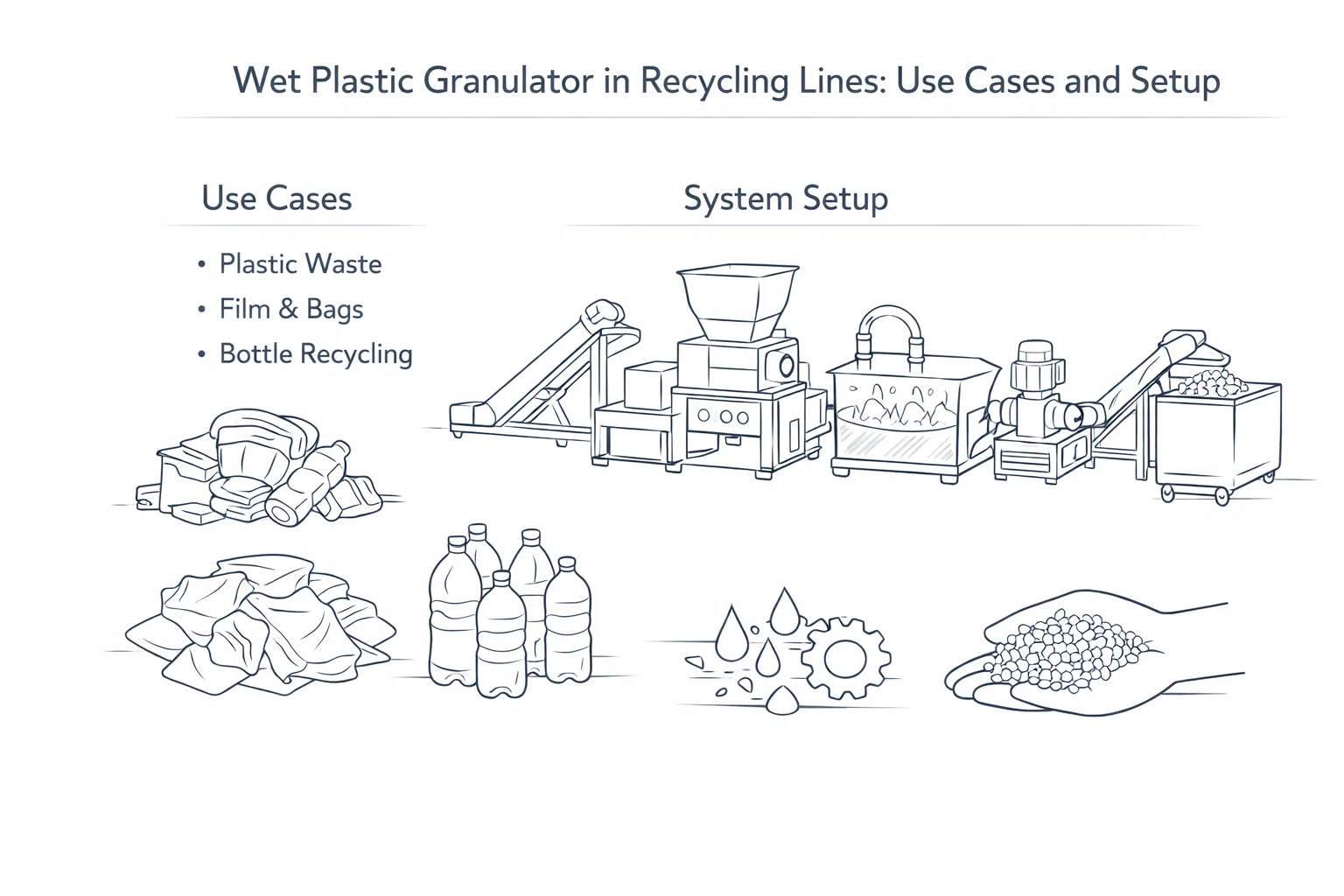
As global demand for recycled plastics grows, efficient processing technologies become critical. Wet plastic granulator machines are at the heart of modern recycling lines because they can shred, crush, and wash contaminated plastic waste in one streamlined step. This guide explains how wet granulation works, highlights its advantages over dry processing, and introduces the key features of our wet plastic granulator systems.
Why Use a Wet Plastic Granulator?
Conventional dry granulation breaks down plastic waste but cannot remove surface contaminants such as labels, dirt, and residues. Wet granulators integrate water into the cutting chamber, allowing the machine to:
-
Break plastic waste into smaller flakes while simultaneously rinsing away dirt and labels
-
Minimize dust generation, improving downstream air quality
-
Reduce friction and heat build‑up, protecting the material from thermal degradation
-
Deliver cleaner, ready‑to‑wash flakes for improved recycling efficiency
This combination makes wet granulation ideal for processing post‑consumer plastics such as bottles, film, and rigid containers.
How Do Wet Plastic Granulator Machines Work?
Wet granulators combine a powerful rotor and stationary blades with a continuous water spray. During operation:
-
Feeding & Pre‑Size Reduction: Contaminated plastics enter the hopper and are grabbed by the rotor.
-
High‑Speed Cutting & Washing: The rotor spins at high speed, shearing the material against fixed blades. Water flushes through the cutting chamber, rinsing away contaminants.
-
Wet Discharge: Cleaned flakes exit via a wet discharge screw or conveyor for further washing or drying.
-
Water Recirculation: The process water can be filtered and recirculated to reduce water consumption.
Properly designed wet granulators deliver continuous throughput with minimal blockages and reduced wear.
Key Features to Look For in Wet Plastic Granulator Systems
Wet plastic granulators should be evaluated on durability, energy use, and maintenance access. Key design features typically include:
-
High-speed rotor stability: A balanced rotor supports consistent cutting and reduces vibration-related wear.
-
Effective wet discharge: A discharge screw or conveyor that removes flakes quickly while draining free water helps stabilize downstream handling.
-
Adequate motor and torque reserve: Sufficient power prevents speed collapse on tougher plastics and improves throughput stability.
-
Wear protection in wet zones: Materials and sealing designed for continuous water exposure reduce corrosion and premature bearing failure.
Applications and Compatible Materials
Wet granulators are versatile and can process a wide variety of plastic wastes, including:
-
HDPE bottles and containers
-
PP crates and caps
-
LDPE/LLDPE film and agricultural film
-
PET bottles (pre‑washing)
-
Mixed rigid plastics with labels or dirt
By incorporating water into the cutting process, these machines deliver cleaner flakes, reducing the load on subsequent washing and separation stages.
Maintenance Tips for Reliable Operation
To keep your wet plastic granulator running smoothly, follow these best practices:
-
Rotor and Knife Inspection: Regularly check blade sharpness and spacing; replace or adjust when necessary.
-
Water System Upkeep: Clean filters and spray nozzles to maintain consistent flow and pressure.
-
Bearing Lubrication: Follow the recommended lubrication schedule to prevent premature wear.
-
Screen Cleaning: Ensure discharge screens remain free of blockages to avoid overheating and output reduction.
-
Check Coupling and Motor: Inspect coupling alignment and motor temperature to prevent damage.
Proper maintenance extends machine life, reduces downtime, and ensures consistent output quality.
Supplier Selection Criteria for Wet Plastic Granulators
When choosing a supplier, prioritize operational reliability and lifecycle support:
-
Configuration fit: Ability to match knife configuration, discharge type, and throughput to your material and layout.
-
Documented references: Evidence of similar installations and feedstock conditions.
-
Spare parts readiness: Clear lead times and recommended critical spares list (knives, screens, bearings, seals).
-
Service response: Commissioning support, troubleshooting process, and maintenance guidance.
-
Commercial clarity: Transparent scope, utilities assumptions (water recirculation), and performance expectations.
Setup Checklist: Integrating a Wet Plastic Granulator in a Recycling Line
Use this checklist to avoid bottlenecks and unnecessary wear when commissioning a wet granulator:
-
Placement in the line: Typically after manual sorting and before float-sink separation or friction washing, so the granulator performs initial size reduction and surface rinse.
-
Water spray and recirculation: Ensure stable spray coverage in the cutting chamber; add filtration (screen/settling) before recirculation to prevent abrasive solids from accelerating knife wear.
-
Discharge handling: Confirm whether you will use a wet discharge screw or conveyor, and match downstream equipment (friction washer, dewatering, or centrifugal dryer) to the wet flake flow rate.
-
Sizing target alignment: Select screen/perforation based on downstream washing and buyer flake specs; overly fine sizing increases fines and load on water treatment.
-
Knife condition and gap checks: Set a routine for blade sharpness and knife clearance verification before throughput ramps up.
-
Commissioning test: Run a short trial with your worst-case feedstock (labels, dirt, moisture variability) and check reject streams and water clarity to validate settings.
Ready to Learn More?
If you’re planning to upgrade your recycling line or start a new project, understanding the role of wet granulation is essential. For detailed specifications and pricing, view our Wet Plastic Granulator details here. Our team will be happy to advise on the right configuration for your needs.