Le polystyrène expansé (PSE), largement utilisé pour les emballages, l'isolation et les contenants alimentaires jetables, est notoirement difficile à recycler en raison de sa légèreté et de son encombrement. Cependant, les machines de recyclage modernes, comme les machines de recyclage de PSE, offrent des solutions efficaces pour la gestion et la valorisation des déchets de PSE. Cet article examine les flux de travail des deux principaux types de machines de recyclage de PSE : le pressage à froid et la fusion à chaud, afin de vous aider à choisir l'équipement le plus adapté à vos opérations de recyclage.
Flux de travail de la machine de recyclage de polystyrène expansé pressé à froid
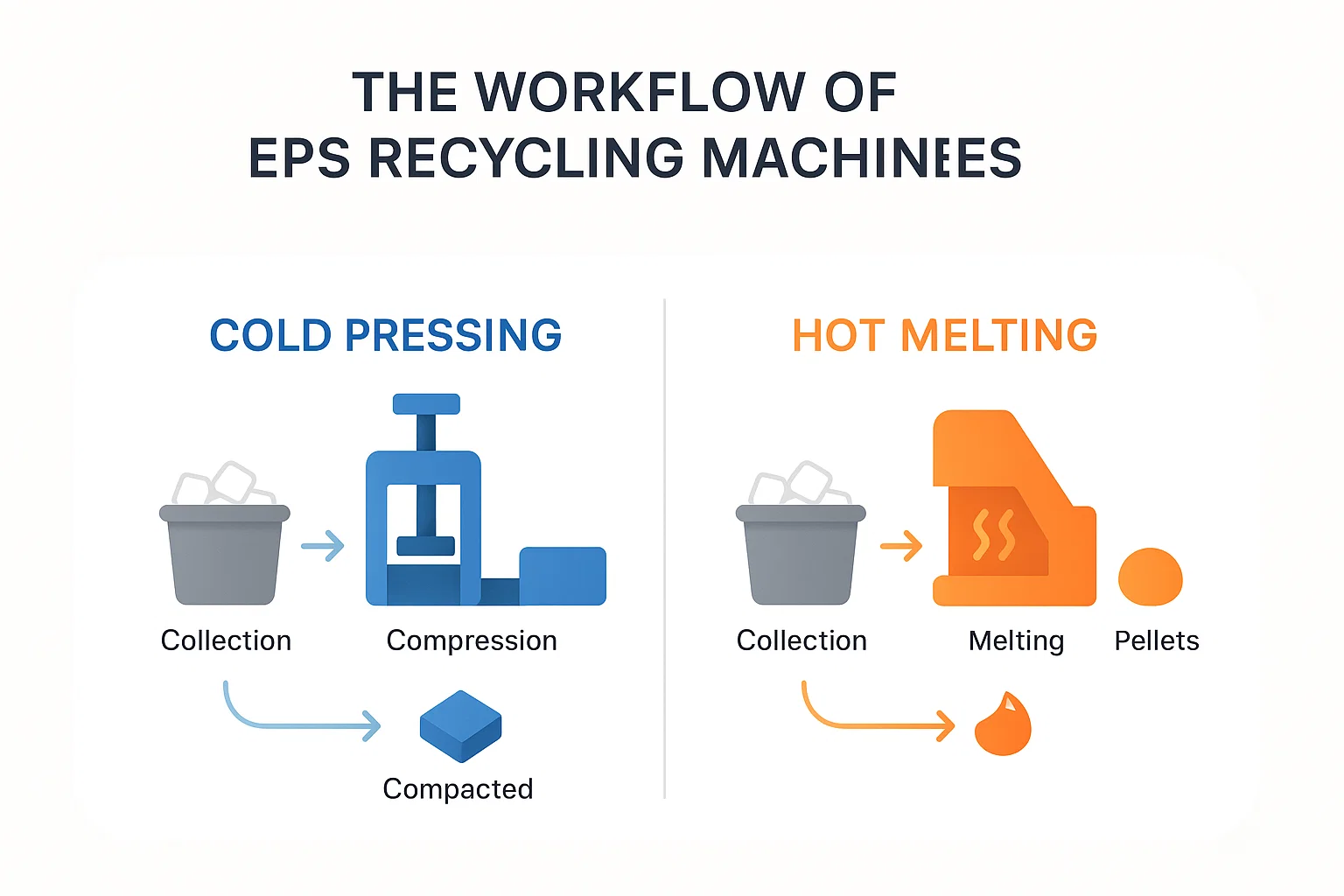
Les machines de pressage à froid, également appelées densificateurs EPS, compactent les déchets EPS mécaniquement sans appliquer de chaleur, réduisant ainsi considérablement leur volume.
- Collecte et tri
La première étape consiste à collecter les déchets de PSE et à s’assurer que les contaminants tels que le ruban adhésif, les étiquettes et la saleté sont éliminés. - Déchiquetage
Les déchets EPS propres sont introduits dans un broyeur, qui les décompose en morceaux plus petits et plus faciles à gérer. - Compression
Le PSE broyé est ensuite introduit dans la chambre de pressage à froid, où il est comprimé mécaniquement sous haute pression. Son volume est ainsi réduit jusqu'à 50:1. - Extrusion en blocs
L'EPS comprimé est extrudé en blocs ou bûches denses et solides, prêts pour un transport et un stockage efficaces.
Avantages :
- Consommation d'énergie réduite.
- Aucune émission liée à la chaleur.
- Adapté aux opérations recherchant simplicité et rentabilité.
Pour des informations détaillées sur les machines de pressage à froid, explorez notre Presse à froid pour mousse EPS page.
Flux de travail de la machine de recyclage de polystyrène expansé à chaud
Les machines de fusion à chaud fonctionnent en faisant fondre les matériaux EPS dans une forme compacte et réutilisable, augmentant considérablement l'efficacité du recyclage.
- Collecte et prétraitement
Similaire au pressage à froid, les déchets EPS sont collectés et nettoyés pour éliminer les contaminants. - Alimentation et broyage
Les matériaux EPS sont introduits dans la trémie de la machine et traités par un concasseur intégré, les réduisant en fragments plus petits. - Processus de fusion
L'EPS broyé entre dans une chambre de chauffage où il est fondu à des températures comprises entre 140°C et 200°C, le transformant en un état liquide. - Extrusion et refroidissement
L'EPS fondu est extrudé à travers une buse, formant des lingots ou des blocs denses à mesure qu'il refroidit et se solidifie.
Avantages :
- Rapport de réduction élevé (jusqu'à 90:1).
- Produit des lingots uniformes et denses adaptés au recyclage en nouveaux produits.
- Gestion efficace de grands volumes de déchets EPS.
Visitez notre site détaillé Machine de fusion de mousse EPS guide pour mieux comprendre les procédés de fusion à chaud.
Analyse comparative : pressage à froid et fusion à chaud
Le choix entre les machines de pressage à froid et de fusion à chaud dépend de plusieurs facteurs opérationnels :
| Fonctionnalité | Pressage à froid | Fusion à chaud |
|---|---|---|
| Rapport de réduction du volume | Modéré (jusqu'à 50:1) | Élevé (jusqu'à 90:1) |
| Consommation d'énergie | Inférieur | Plus haut |
| Qualité du produit final | Blocs solides comprimés | Lingots uniformes aptes à être réutilisés |
| Impact environnemental | Émissions de chaleur minimales | Plus élevé en raison du processus de chauffage |
Choisir la machine de recyclage EPS adaptée à votre entreprise
Tenez compte de votre taille opérationnelle, de votre budget disponible et de vos objectifs de recyclage lors du choix de votre machine de recyclage de PSE. Le pressage à froid offre simplicité et coûts d'exploitation réduits, idéal pour les petites entreprises ou celles produisant peu de déchets de PSE. En revanche, la fusion à chaud convient aux entreprises exigeant des rendements plus denses et une meilleure efficacité de recyclage.
Conclusion
Les machines de recyclage de PSE d'Energycle, tant par pressage à froid que par fusion à chaud, offrent des solutions durables et pratiques, adaptées à vos besoins de recyclage industriel. En investissant dans des équipements adaptés, les entreprises peuvent bénéficier d'importants avantages environnementaux et économiques tout en renforçant leur engagement en faveur du développement durable.
Pour discuter des solutions de recyclage EPS les plus adaptées à vos besoins, contactez notre équipe d'experts dès aujourd'hui !